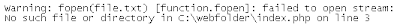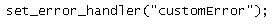Basic Use of Exceptions
In the example below, when an exception is thrown, it will not be executed, and PHP will try to find the matching "catch" block. If an exception is not caught, a fatal error will be issued with an "Uncaught Exception" message. Now, I will let you try to throw an exception without catching it and see what kind of error that you will get:

(click image to view)
############################################################
The Output:
Fatal error: Uncaught exception 'Exception'
with message 'Value must be 5 or below' in C:\webfolder\index.php:6
Stack trace: #0 C:\webfolder\index.php(12):
checkNum(28) #1 {main} thrown in C:\webfolder\index.php on line 6
############################################################
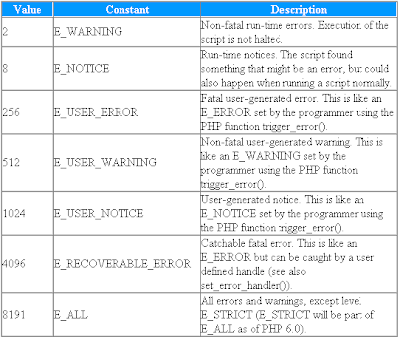
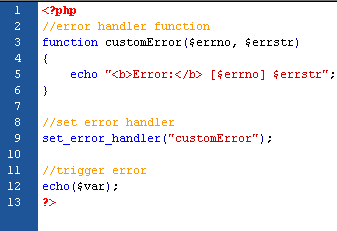
To avoid the error from the example above, we need to create the proper code to handle an exception. Proper exception code should include:
- Try - A function using an exception should be in a "try" block. If the exception does not trigger, the code will continue as normal. However if the exception triggers, an exception is "thrown".
- Throw - This is how you trigger an exception. Each "throw" must have at least one "catch".
- Catch - A "catch" block retrieves an exception and creates an object containing the exception information.
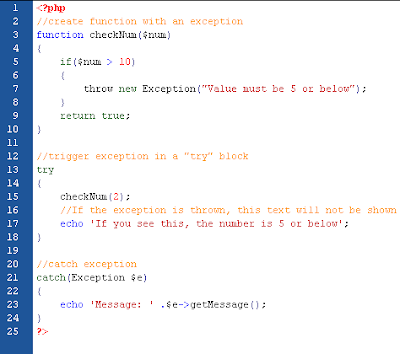
(click image to view)
############################################################
The Output:
Message: Value must be 5 or below
############################################################
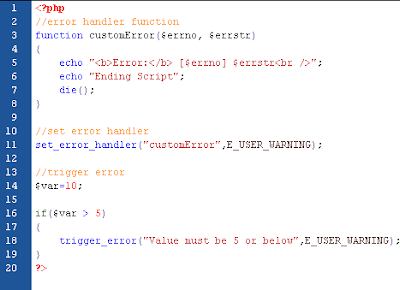
The code above throws an exception and catches it:
- The checkNum() function is created. It checks if a number is greater than 10. If it is, an exception is thrown.
- The checkNum() function is called in a "try" block.
- The exception within the checkNum() function is thrown.
- The "catch" block retrives the exception and creates an object ($e) containing the exception information.
- The error message from the exception is echoed by calling $e->getMessage() from the exception object.
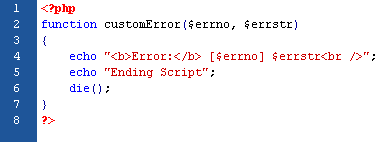
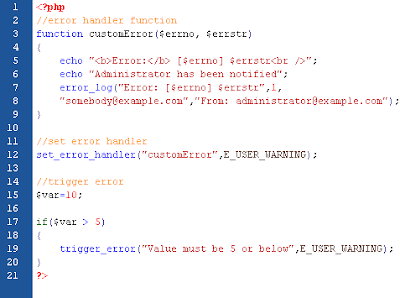
Creating a Custom Exception Class
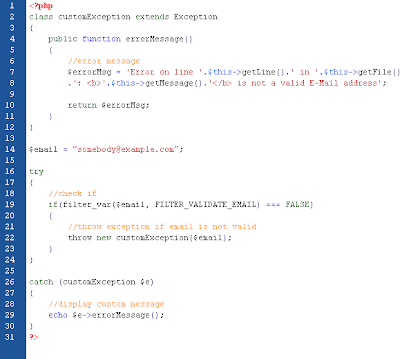
(click image to view)
The code above throws an exception and catches it with a custom exception class:
- The customException() class is created as an extension of the old exception class. This way it inherits all methods and properties from the old exception class.
- The errorMessage() function is created. This function returns an error message if an e-mail address is invalid.
- The $email variable is set to a string that is not a valid e-mail address.
- The "try" block is executed and an exception is thrown since the e-mail address is invalid.
- The "catch" block catches the exception and displays the error message.
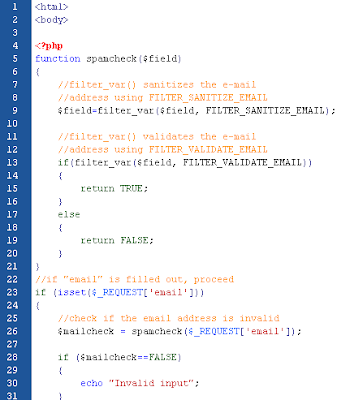
Multiple Exception
It is possible for a script to use multiple exceptions to check for multiple conditions. It is possible to use several if..else blocks, a switch, or nest multiple exceptions. These exceptions can use different exception classes and return different error messages:
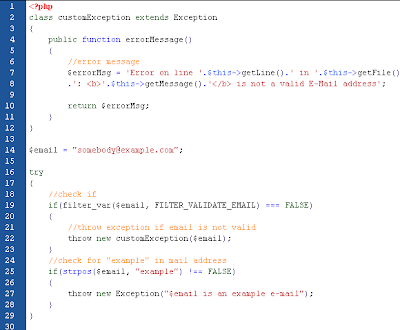
(click image to view)
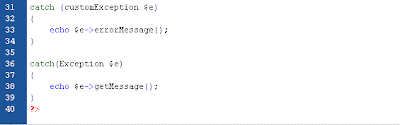
(click image to view)